Choosing and publishing images of refugees, migrants and people in distress is both painful and difficult, notably when they’re graphic and reach various audiences across multiple media platforms in record time.

The image as symbol (courtesy “A Sea of Images”)
Weighty decisions may lead to photos becoming icons and symbols representing all other victims as that of Aylan Kurdi, the Syrian toddler lying face down on a Turkish beach in 2015 that went viral in just three hours.
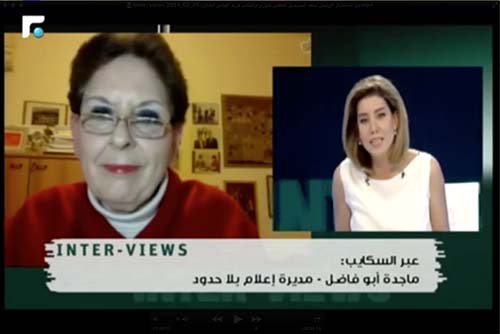
Media Unlimited director Magda Abu-Fadil discussed the ethical implications and how such pictures can also be (mis)used by politicians to score points and advance their own agendas.

Magda Abu-Fadil (left) discusses the ethics of using photos of migrants, refugees (courtesy Tom Law)
The topic made for an animated discussion during “Movie Night” hosted by the Ethical Journalism Network (EJN) at the December 2017 Arab Reporters for Investigative Journalism’s (ARIJ) annual conference in which she participated as a panelist.
The movie in question was “A Sea of Images,” a documentary on how media tackle migrants and refugees from the Middle East and Africa fleeing their troubled lands in a perilous journey across the Mediterranean Sea to Europe.
The film, produced by Misja Pekel and Maud van de Reijt, is part of a series for Dutch public television that examined the connection between media and public opinion.

How do editors decide what photos to publish? (courtesy A Sea of Images)
Refugee fatigue, she argued in the discussion following the film’s showing, can affect journalists’ and editors’ judgment in their choice and dissemination of images, with ethics falling by the wayside.

Audience debates ethics of photo publishing (courtesy Tom Law)
Aidan White, veteran journalist and director of the Ethical Journalism Network, said three of the Aylan Kurdi pictures were published around the world, but photos could be used in different ways to tell different narratives.
“What that reveals, is that although the pictures are dramatic and important, in the end it’s the context in which the pictures are used by journalists,” White explained.

Aidan White on the ethical use of images (courtesy “A Sea of Images”)
The ethical use of images depicting migrants, refugees and vulnerable people in the media, and what impact they have on public policy, will continue to trigger debate so long as conflicts, economic and natural disasters cause massive population displacement.